Nvidia has won the 3D Occupancy Prediction Challenge for autonomous driving development set out by the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Conference (CVPR), in Vancouver, Canada.
The 3D Occupancy Prediction Challenge required teams to develop algorithms which used only camera input for inference. Teams could use open-source data sets and models to facilitate the exploration of data-driven algorithms and large-scale models. Additionally, CVPR provided a baseline sandbox for the latest state-of-the-art 3D occupancy prediction algorithms in real-world scenarios. The competition saw more than 400 submissions from nearly 150 international teams.
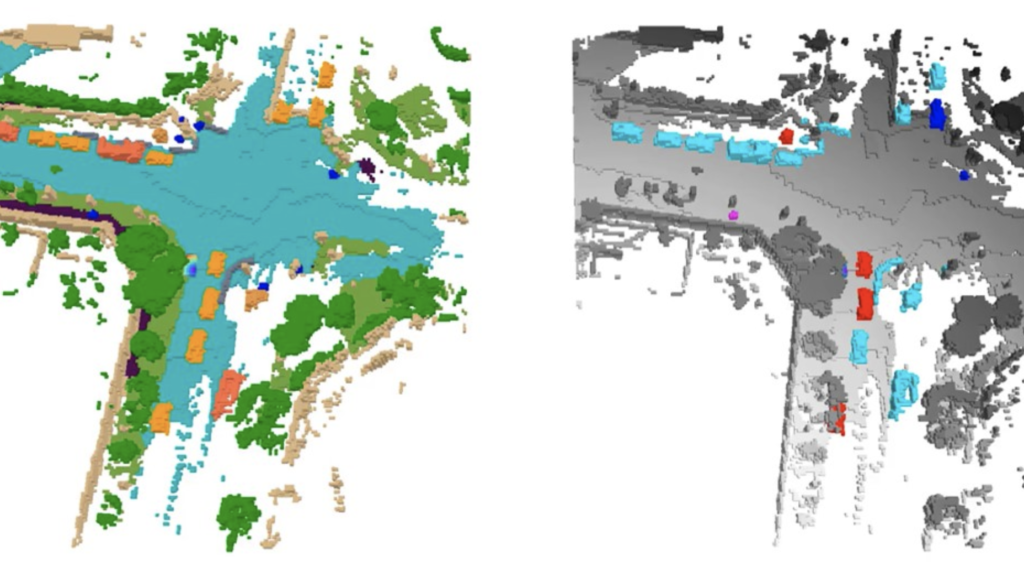
3D occupancy prediction is described as the process of forecasting the status of each voxel in a scene or each datapoint on a 3D bird’s-eye-view grid. Voxels are identified as free, occupied or unknown. 3D occupancy grid prediction is vital when working on the development of safe and reliable self-driving systems as it provides an array of information to AV planning and control stacks which utilize neural networks and transformer models, enabled by the Nvidia Drive platform.
“Nvidia’s winning solution features two important AV advancements,” said Zhiding Yu, senior research scientist for learning and perception at Nvidia. “It demonstrates a state-of-the-art model design that yields excellent bird’s-eye-view perception. It also shows the effectiveness of visual foundation models with up to 1 billion parameters and large-scale pre-training in 3D occupancy prediction.”
While conventional 3D object detection is a core task in AV perception, it has its limitations, such as lack of expressiveness. This means the bounding boxes may not represent sufficient real-world information. Furthermore, this also requires defining taxonomies and ground truths for all possible objects – including rare real-world occurrences, such as objects which may have fallen off a vehicle. 3D occupancy prediction, however, delivers rich information about the surrounding world and environment to a self-driving vehicle’s planning stack – a necessity for end-to-end autonomous driving.
For more Nvidia news, click here.