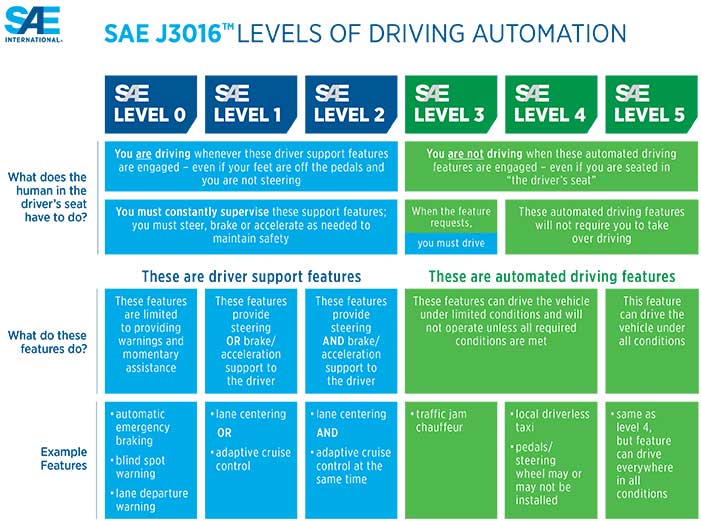
What’s the difference between automated and fully-automated driving? How different is Level 3 to Level 5 and 6? As autonomous driving technologies and assistance systems evolve and are introduced into vehicles, understanding the taxonomy and definitions related to these systems is key to providing a clearer picture for both the consumer and manufacturer.
The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), an international organization that educates and helps develop standards for professional engineers, famously created a regulatory framework and best practices guide for automated driving systems. The SAE J3016 employs levels ranging from 0-5 to indicate the difference in driver support systems and automated driving features.
Used to guide manufacturers and other entities in the design, development, testing and deployment of highly-automated vehicles, the document became the de facto global standard for AV technology. The US Department of Transportation (DoT), for example, adheres to J3016’s six levels of automation for on-road motor vehicles in its Federal Automated Vehicles Policy.
Despite the breakdown in levels, however, some confusion still remains among consumers as to what constitutes a ‘self-driving’ car and what amount of driver input is required, regardless of how capable an ADAS may be. Tesla’s Autopilot, for example, which enables the car to drive itself, controlling both steering and braking, is often confused with an assistance system where drivers can engage in another activity while driving. However, it is a Level 3 system that requires drivers to remain in the driving seat and to be ready to take control. It is not until vehicles reach Level 4 where occupants are not required to take over driving duties and vehicles may not even feature a steering wheel.
To help clarify these definitions, SAE International has updated its J3016 with an infographic that is able to visually show the difference in the levels of autonomy and provide examples of where they may be found.
“The new chart offers more consumer-friendly terms and definitions for the levels, which are frequently cited and referred to by industry and media. The infographic will help to eliminate confusion by providing clarity and using terms more commonly used by consumers,” SAE International said in a press release.
The chart explains more clearly what the driver is required to do with each level, what a vehicle with each level of autonomy can do, and the types of typical technology.